Monogenic diseases
Neuromuscular diseases
Our focus here are patients with inborn arthrogryposis (contractures = bending of joints) and pterygia (webbing). Most of them have also reduced muscular strength and suffer from additional problems as respiratory distress.
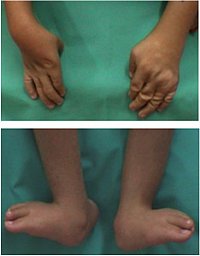
Neuromuscular diseases 1
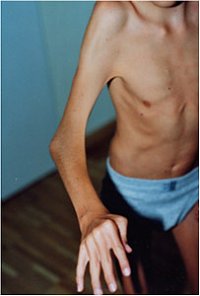
Neuromuscular Diseases 2
Neuromuskulr 3
Nuclear lamina associated diseases
The chromatin-lamina network is increasingly studied due to the growing number of phenotypes found in mutations of Lamin A, B1 or B2 such as Hutchison Gilford Progeria, subtypes of cardiomyopathy, muscular dystrophy, CMT, lipodystrophy, or leukodystrophy. It has suspected impact on mitosis, gene expression and aging.
The lamin B receptor (LBR) is an inner nuclear membrane protein that interacts with chromatin and lamins, and has sterol reductase activity. We identified mutations in the lamin B receptor gene in human Pelger Anomaly and recessive ichthyosis in mice.
LBR mutations cause a wide range of phenotypes affecting blood, bones, skin, brain morphology and general growth. However, the mechanisms are poorly understood. Studying clinical and cellular variability in LBR mutations might point us to potential modified and modifying genes and proteins within the network of lamins, chromatin, methylation, and sterol metabolism.
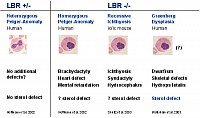
Laminopathie, Tabelle




